¶ Wi-Fi
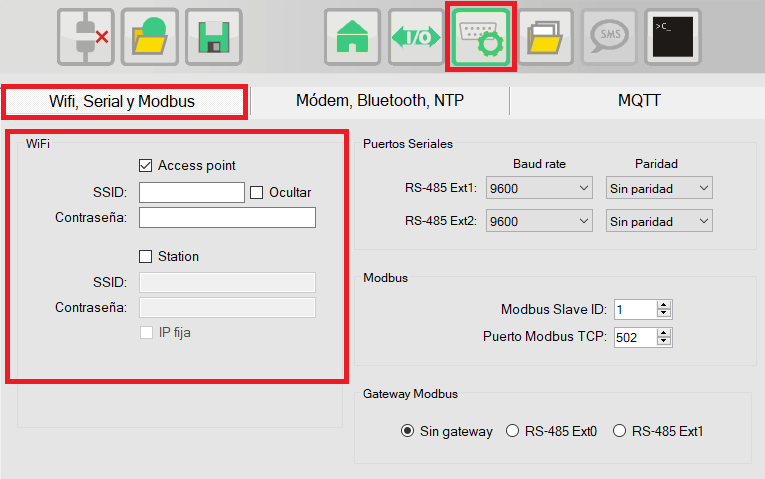
In the communications window, in the tab "Wifi, Serial and Modbus" you can configure the parameters related to the wifi interface.
Here you can select the operating mode from the following options:
- Off
By deselecting the Access point and Station check-boxes, the Wi-Fi module is turned off and is not used. - Access Point
The RTU-X creates a Wi-Fi network with the configured SSID and password and then accepts connections from other devices. In this configuration, the RTU-X address is always 192.168.4.1 and DHCP is enabled, that is, the RTU-X assigns an IP to the devices that connect to the access point. If the password is left empty, the access point will be open and without security. There is the option to hide this network so that it is not visible to other devices, but remains accessible if you know the SSID and password. - Station
- Fixed IP OFF (uses DHCP)
The RTU-X connects to the Wi-Fi network with the configured SSID and password, and takes the IP of the access point to which it connects. - Fixed IP ON (Static IP address)
The RTU-X connects to the Wi-Fi network with the configured SSID and password, and uses the network settings that it has configured (IP, subnet, Gateway and DNS).
- Fixed IP OFF (uses DHCP)
The RTU-X allows the possibility of being in Access Point and Station mode at the same time.
¶ RS-485 serial bus
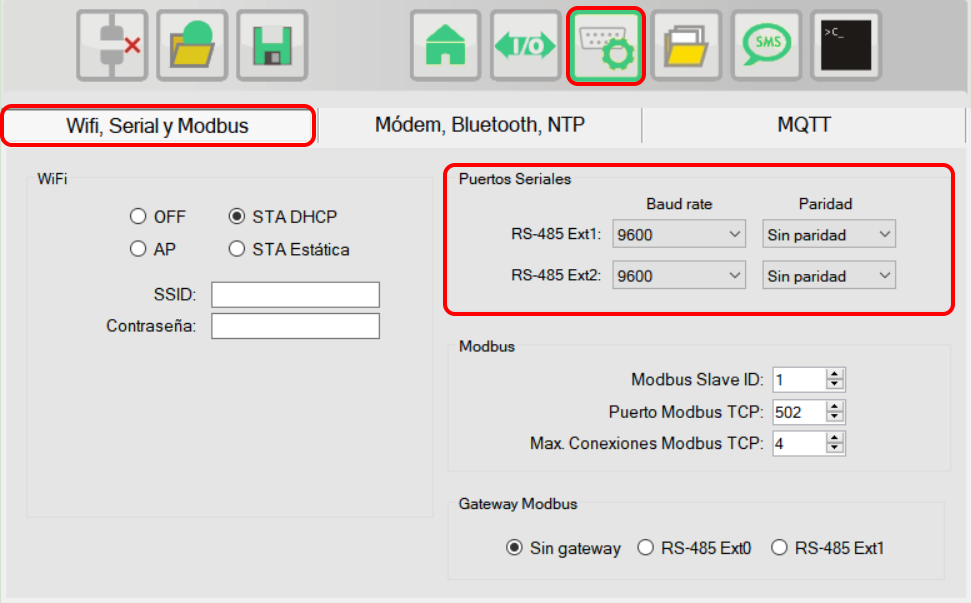
In the communications window, in the tab "Wifi, Serial and Modbus" you can configure the parameters related to the RS-485 serial interfaces.
The RS-485 serial interfaces are optional expansion modules. For each interface, speed and parity can be configured.
¶ Modbus
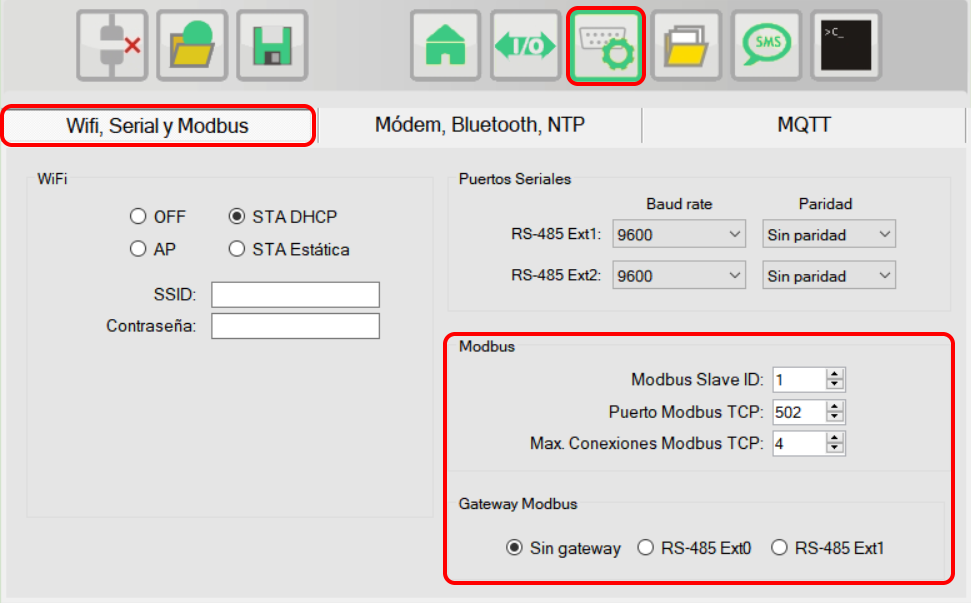
In the communications window, in the tab "Wifi, Serial and Modbus" you can configure the parameters related to Modbus.
The parameters are:
- Modbus Slave ID
The Modbus slave number of the RTU-X (by default 1). - Modbus TCP port
In the case of Wi-Fi connections, the TCP port to use (by default 502). - Max. Modbus TCP connections
The maximum number of simultaneous Modbus TCP incoming connections that the RTU-X accepts (by default 4). - Modbus gateway
Defines the default communication interface to which all Modbus messages whose recipient does not match the Slave ID of the RTU-X are forwarded. If the option "No gateway" is selected, the RTU-X will respond with an error message to all Modbus packets that are not for it. Otherwise, it will forward them over the RS-485 bus depending on which one is selected and then forward the reply back to the sender. Through this functionality, the RTU-X can act as an intermediary so that a client can communicate transparently with a device connected to the RS-485 bus in the expansion modules.
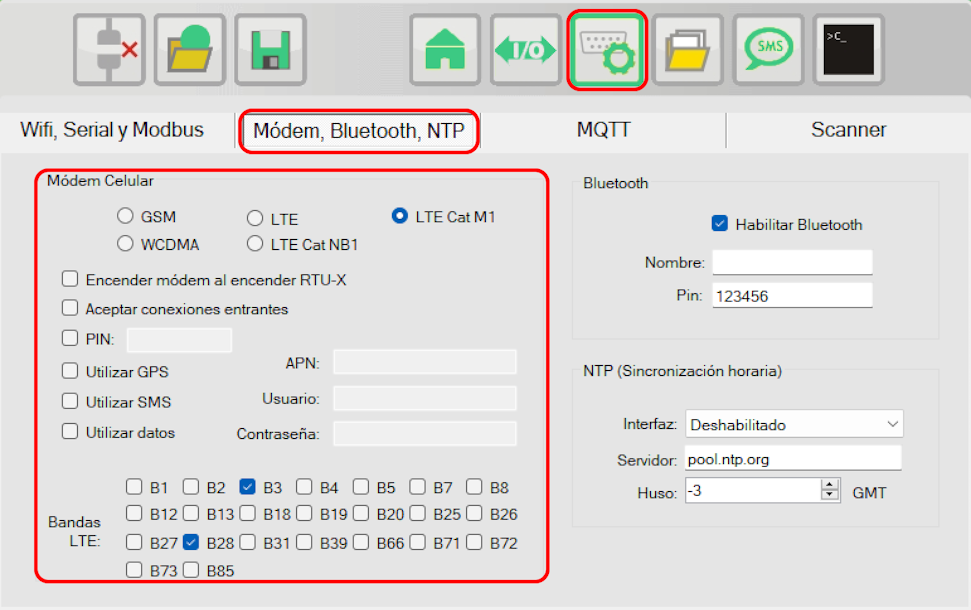
¶ Modem
In the communications window, in the tab "Modem, Bluetooth, NTP" you can configure the parameters related to the modem. The modem is an optional module.
The parameters that can be configured are:
- Network to use
User may choose between different modem modules which support several technologies and communication bands:- Quectel BG95: LTE Cat-NB1 or LTE Cat-M1 with down grade to 2G.
- Cat M1 / NB-IoT - B1/B2/B3/B4/B5/B8/B12/B13/B18/B19/B20/B25/B26/B27/B28/B31/B66/B71/B72/B73/B85
- EGPRS 850/900/1800/1900 MHz
- Quectel EG91: LTE with down grade to 3G / 2G.
- LTE - B1/B2/B3/B4/B5/B7/B8/B28/B66
- WCDMA - B1/B2/B5/B8
- EGPRS 850/900/1800/1900 MHz
- Quectel BG95: LTE Cat-NB1 or LTE Cat-M1 with down grade to 2G.
- Modem on at power-up
This is the normal operating mode in cases where the RTU-X is always on and connected to a stable power source. If this option is disabled, it is possible to control the modem on and off from the script by means of the modem_on variable. This case is often used in applications where power consumption is critical, and you want to turn on the modem for short periods of time just to send the information stored in the log. - Accept incoming connections
When this option is checked, the RTU-X accepts incoming connections on the port 502 used by the user interface. By default, this options is disabled. - PIN
The PIN to be asigned in case the SIM requires it. - Enable GPS
Set this option to enable GPS. The GPS information is available in variables in the script. - Enable SMS
This option must be enabled if you want to send and receive SMS. - Enable data
This option must be enabled for the modem to establish the data connection with the configured APN. - LTE Bands
Definition of bands to be used when LTE is used to connect to the cellular network.
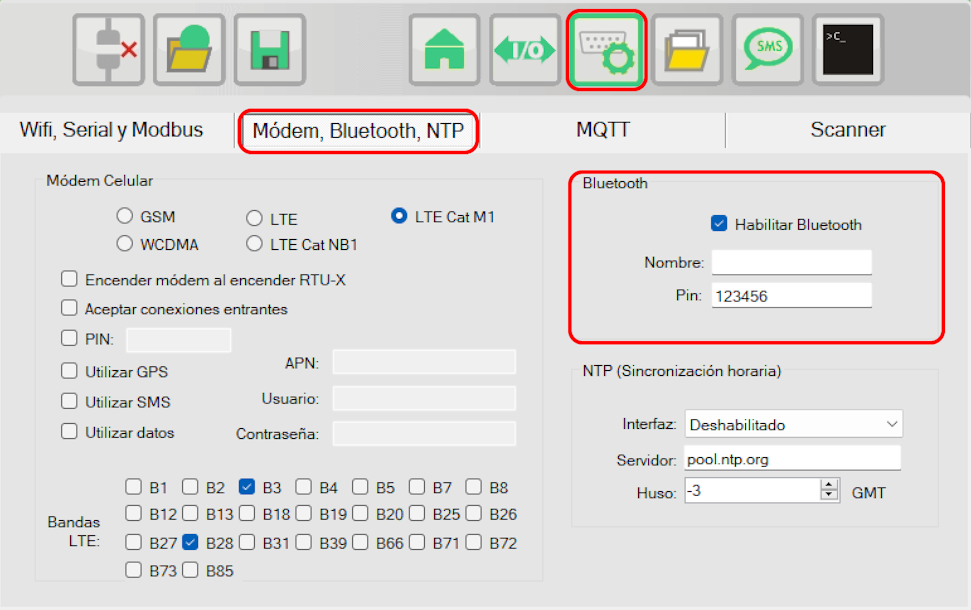
¶ Bluetooth
By default the RTU-X has BLE 4.2 connectivity that can be used to connect to the device from the configuration software and also to act as a master of other BLE devices, such as temperature and humidity sensors.
In the communications window, in the tab "Modem, Bluetooth, NTP" you can configure the parameters related to Bluetooth.
You must select the name of the device (it will be the name advertised by the RTU-X) and the security pin, which will be requested when connecting.
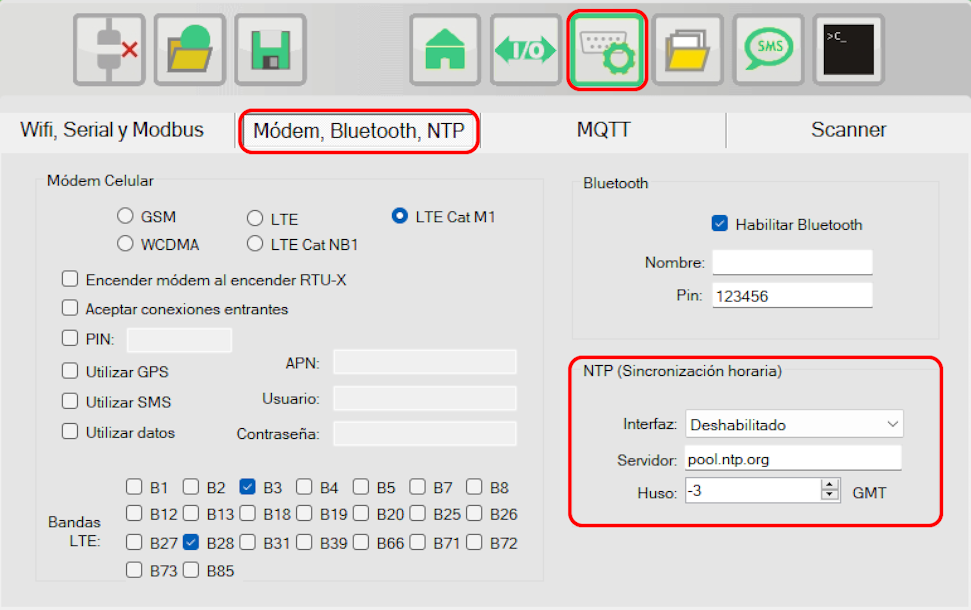
¶ NTP
In the communications window, in the tab "Modem, Bluetooth, NTP" you can configure the configuration of an NTP server for time synchronization.
You must select:
- Interface
It can be wi-fi, modem or the same interface being used for the MQTT connection - Server
URL or IP address of the NTP server - Time zone
Relative to UTC
¶ MQTT
The MQTT protocol is a communications protocol over TCP/IP that has been adopted as one of the most widely used standards for IoT devices.
The RTU-X uses MQTT to send the log records to a server in the cloud, but it is also used to perform other more complex functions when the RTU-X is connected to Thingsboard; such as updating all settings, synchronizing shared variables, or sending RPC commands.
¶ MQTT configuration
The parameters to configure for the MQTT connection are the following:
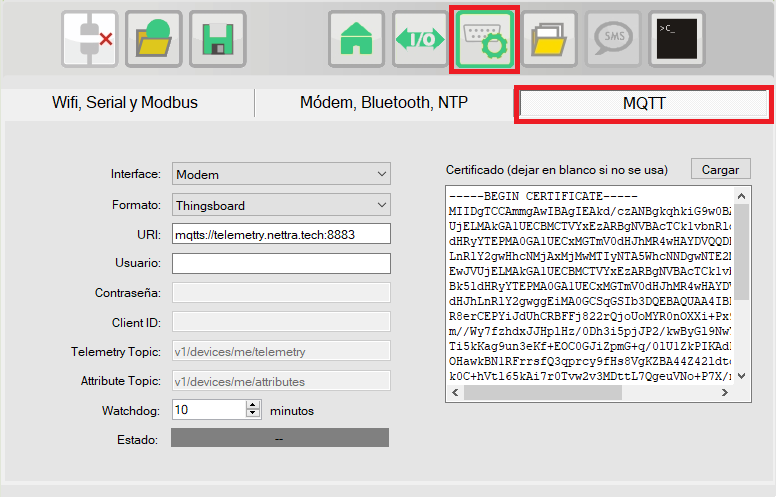
- Interfce - The RTU-X implements the MQTT protocol over Wi-Fi and the modem data connection. The physical interface to use must be selected.
- Format - The following options are available:
- JSON - It uses the JSON format to send the log records.
- Ultralight - It uses the Ultralight 2.0 format for sending the log records.
- Predix - It uses the JSON format compatible with the General Electric's MQTT Data Collector according to the specified here.
- Thingsboard - In this option, the RTU-X is configured to establish the connection with a Thingsboard server. Nettra Telemetry+ is a professional instance of Thingsboard managed by Nettra.
- URI – The URI must have the format "equema://host:port" where schema can be mqtt or mqtts depending on whether or not you want to establish an SSL connection. An example URI is mqtts://myhost.com:8883
- User, password and client ID – According to the MQTT protocol.
- Telemetry Topic – Defines the MQTT topic to which the stored records are sent using the log and report functions of the script for telemetry type variables.
- Attribute Topic – Defines the MQTT topic to which the stored records are sent using the log and report functions of the script for variables of type attribute.
- Watchdog – It allows to implement a security mechanism in case of communication failure. If the RTU-X is unable to establish the MQTT connection for this time, it will restart automatically. If the configured time is zero, this functionality is disabled.
- Certificate – Server certificate in PEM format in case of using SSL for MQTT connection. Leave blank if not used.
For the Thingsboard format option, you only need to configure the URI, user (token) that uniquely identifies the device on the platform and certificate (in case of using mqtts). All other parameters are set automatically.
When using the Telemetry + instance of Nettra, you must select the Thingsboard format and fill in only the user (token) that will be provided by Nettra. The URI and certificate are the values that are loaded by default when selecting Thingsboard.
To send variables through MQTT you can use the log and report functions from the script. Both functions can be used with variables of type telemetry or attribute.
¶ Integration with Thingsboard
When Thingsboard is selected as the format for the MQTT connection, the RTU-X implements additional functionalities in addition to sending the log by MQTT.
These functionalities are described below.
¶ “Shared” attributes
When a variable in the script is defined with the prefix shared, the value of the variable is synchronized with the value of the shared attribute in Thingsboard with the same name if it exists.
This is achieved without the user having to do anything special because when establishing the MQTT connection, the RTU-X automatically subscribes to the topics.
¶ Periodic submission of internal attributes
The RTU-X automatically publishes a list of useful internal variables to the server.
The following variables are published every time the connection is established with the MQTT server:
| Variable | Detalle |
| model | RTU-X model (DIN or IP68) and hardware version |
| mac_wifi | MAC address of the Wi-Fi module. |
| ext1 | Information of the module connected in the extension socket 1. |
| ext2 | Information of the module connected in the extension socket 2. |
| modem_imei | Modem IMEI (if a modem is present in the communication socket). |
| modem_imsi | IMSI of the SIM (if a modem is present in the communication socket). |
The following variables are published periodically every 10 minutes:
| Variable | Detalle |
| battery | Battery percentage. |
| battery_status | Working status of the RTU-X related to battery. It can be Charged, Charging or No power. |
| internal_temperature | Internal temperature of the RTU-X |
| modem_signal | Modem signal level in dBm. |
| wifi_signal | Wi-Fi signal level in dBm. |
¶ Telemetry publication
The following table describes the JSON format used to publish telemetry via MQTT for each possible format.
| Format | Telemetry type variable |
| JSON and Thingsboard |
where XXX is the timestamp in UTC in unix format in milliseconds of the records |
| Ultralight 2.0 |
where TTT is the timestamp in UTC in ISO8601 format |
| Predix |
|
All log records created with the same date / time are sent in the same MQTT package.
If the connection is lost, all records are stored in the log and sent when the connection is re-established.
¶ Attributes publication
| Format | Variable attribute |
| JSON y Thingsboard |
|
| Ultralight 2.0 |
|
| Predix |
|
¶
RPC Commands
RPC stands for “Remote Procedure Call” and is used to send commands and queries from the Thingsboard server to the RTU-X. In the following, the available RPC commands are described.
¶ Format Thingsboard
| Function | Description | Command | Response |
| set | Modify a telemetry, attribute or shared variable |
where NAME is the name of the variable and VALUE the value |
|
| get | Query a telemetry, attribute or shared variable |
where NAME is the name of the variable |
|
| resend_log | Resends the last N log registers |
where N is the number of log registers to resend |
OK |
| unixtime | Sets the RTU-X time in GMT-0. T represents the current timestamp in Unix format. |
|
|
| localtime | Sets the local time of the RTU-X using the year, month, day, hour, minute, and second of the current moment. |
|
|
| timezone | Sets the timezone of the RTU-X |
where t is the new time zone |
OK |
| reset | Resets de RTU-X |
|
None |
| calendarEvents |
Defines calendar events that assign values to the calendar variables declared in the script. When |
|
None |
¶ Format JSON
| Function | Description | Command | Response |
| set | Modifies a variable of type telemetry, attribute, or shared, where NAME is the variable name and VALUE is its value. |
|
|
| get | Queries a telemetry, attribute, or shared variable, where NAME is the variable name. |
|
|
| resend_log | Requests the retransmission of the last N records stored in the event log. |
|
|
| unixtime | Sets the RTU-X time in GMT-0. T represents the current timestamp in Unix format. |
|
|
| localtime | Sets the local time of the RTU-X using the year, month, day, hour, minute, and second of the current moment. |
|
|
| timezone | Sets the timezone of the RTU-X, where N is the new time zone. |
|
|
| reset | Resets the RTU-X |
|
None |
¶ Format Ultralight
| Function | Description | Command | Response |
| set | Modifies a variable of type telemetry, attribute, or shared, where NAME is the variable name and VALUE is its value |
|
|
| get | Queries a telemetry, attribute, or shared variable, where NAME is the variable name. |
|
|
| resend_log | Requests the retransmission of the last N records stored in the event log. |
|
|
| unixtime | Sets the RTU-X time in GMT-0. T represents the current timestamp in Unix format. |
|
|
| localtime | Sets the local time of the RTU-X using the year, month, day, hour, minute, and second of the current moment. |
|
|
| timezone | Sets the timezone of the RTU-X, where N is the new time zone. |
|
|
| reset | Resets the RTU-X |
|
None |
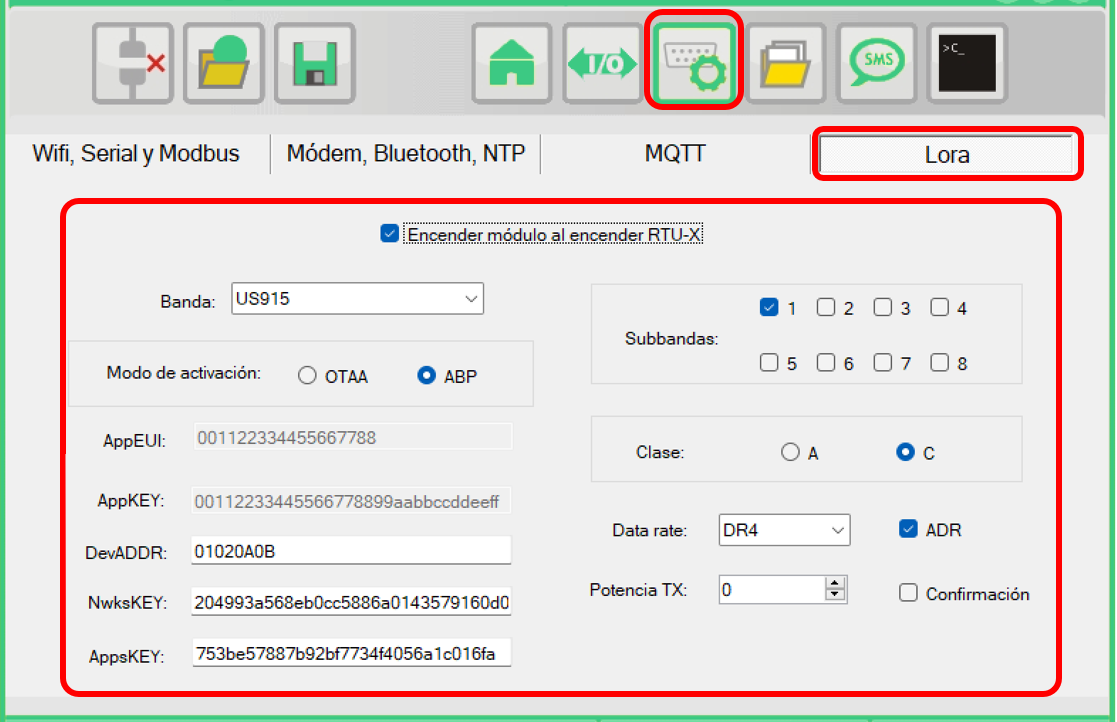
¶ LoraWan
The RTU-X can connect to a LoRaWAN network. To do this, a RAK3172 module must be installed in the WAN socket, to which an external antenna can be connected.
- Powering on the module when the RTU-X starts
This is the normal operating mode when the RTU-X is always on and connected to a stable power source.
If this option is disabled, it is possible to control the module’s power on/off state from the script using the modem_on variable.
- Band
It is possible to select between US915 and AU915 bands.
- Sub-bands
Sub-bands enable groups of eight consecutive channels.
That is, sub-band 1 enables channels 0–7, sub-band 2 enables channels 8–15, and so on.
- Activation mode
It is possible to select between OTAA and ABP.
- Class
Depending on the power-consumption constraints of the solution, you can select between Class A and Class C.
- Data rate
Allows you to select the data rate to use according to the chosen band.
- ADR (Adaptive Data Rate)
Enables or disables this feature.
- Acknowledgment
Enables or disables the sending of messages that request confirmation.
- Keys and addresses
The keys and addresses required to establish a connection with a LoRaWAN network (AppEUI, AppKey in OTAA mode, and DevAddr, NwksKey, AppsKey in ABP) must be defined by the user.
The DevEUI of the device is the one defined by the module manufacturer and can be obtained on the main tab when the module is enabled.
¶ Data transmission and reception
As with MQTT, when using LoRaWAN there are mechanisms for exchanging data with an IoT platform.
To differentiate between data types and commands, several ports are used, as shown in the following table.
| Puerto | Descripción |
| 100 | It is used for publishing data stored in the event log when the log and report functions are executed in the script. |
| 101 | It is used to publish client attributes, that is, the variables declared as attribute in the script. |
| 102 | It is used to receive shared attribute values. |
| 103 | It is used to request the update of shared attributes. |
| 104 | It is used for the implementation of RPC commands and their corresponding responses. |
¶ Data coding
Since the names of the variables being transmitted are user-defined in the RTU-X script (variables of type telemetry), it is necessary to include both the variable names and their values in the transmission. Therefore, to send and receive data while minimizing overhead, a variant of the Ultralight format is used.
In all data packets containing more than one element, those elements are separated by the “|” character.
For example, attributes are reported as name|value.
¶ Telemetry publication
When the log or report statement is executed in the script using variables of type telemetry, the values are stored in the RTU-X event log.
If a connection with a gateway is established, the data is transmitted immediately using a payload with the following format:
ts|key1|value1|key2|value2|...|keyN|valueNHere, ts is the Unix timestamp corresponding to the moment when the log statement was executed.
keyN and valueN represent the name and value of each reported variable, respectively.
¶ Attributes publication
If the log statement is used with attribute variables, the same format is applied but without a timestamp.
key1|value1|key2|value2|...|keyN|valueN¶ RPC commands
It is possible to execute RPC commands via LoRaWAN. The following table shows the implemented commands.
| Function | Description | Command | Response |
| set | Modifies a variable of type telemetry, attribute, or shared, where NAME is the variable name and VALUE is its value |
|
|
| get | Queries a telemetry, attribute, or shared variable, where NAME is the variable name. |
|
|
| resend_log | Requests the retransmission of the last N records stored in the event log. |
|
|
| unixtime | Sets the RTU-X time in GMT-0. T represents the current timestamp in Unix format. This is only applicable if the device is configured as Class C. |
|
|
| localtime | Define la hora local del RTU-X a partir de año, mes, día, horas, minutos y segundos del instante actual. This is only applicable if the device is configured as Class C. |
|
|
| timezone | Sets the local time of the RTU-X using the year, month, day, hour, minute, and second of the current moment. |
|
|
| reset | Resets the RTU-X. |
|
Sin respuesta |
(*) solo tiene sentido su utilización si se configura operación en clase C.
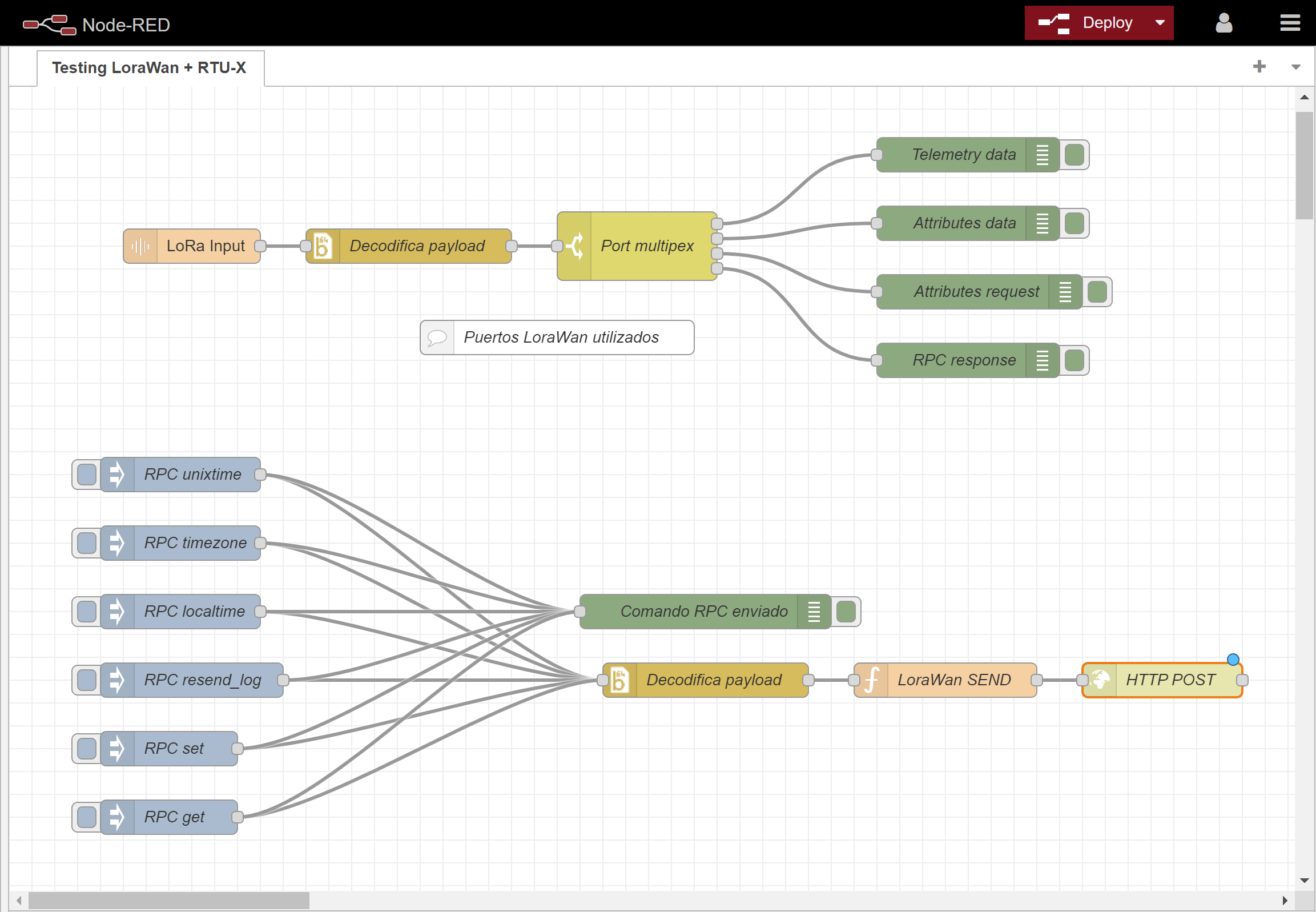
¶ Testing with Milesight Gateway and Node-Red
Below is a Node-Red flow used to test data transmission and reception.
In this setup, an HTTP node is used to execute a POST method that places data into the sending queue for the device connected via LoRaWAN.
For the flow to work correctly, it is necessary to configure the RTU-X DevEUI. The RTU-X must also be registered on the gateway so that incoming data is routed into the flow. Additionally, you must configure the gateway’s IP address and the correct credentials to obtain the JWT token required for the HTTP POST request to function properly.